工作的需要可能要打包.bundle或者相关的MacOS的动态库,故做一个这样子的笔记。
一.mach-o文件介绍
二.文件结构
- Executable:应用的主要二进制
- Dylib Library:动态链接库(又称DSO或DLL)
- Static Library:静态链接库
- Bundle:不能被链接的Dylib,只能在运行时使用dlopen( )加载,可当做macOS的插件
- Relocatable Object File :可重定向文件类型
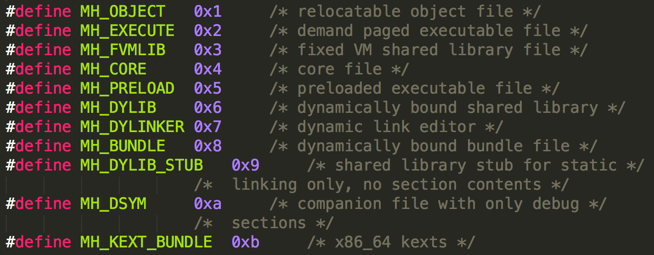
- MH_OBJECT (0x1 )
- 目标文件(.0)
- 静态库文件(.a),静态库文件其实就是多个.o文件的合集.比如支持多种cpu建构的.a库文件.
- MH_EXECUTE (0x2) 可执行文件,
- 比如.app文件
- MH_DYLIB 动态库文件
- .dylib文件
- .framework/xx文件
- MH_DYLINKER (0x7) 动态链接编辑器
- usr/lib/dyld
- MH_DYSM 符号文件
- dSYM/Content/Resources/DWARF/xx常用与app崩溃信息分析
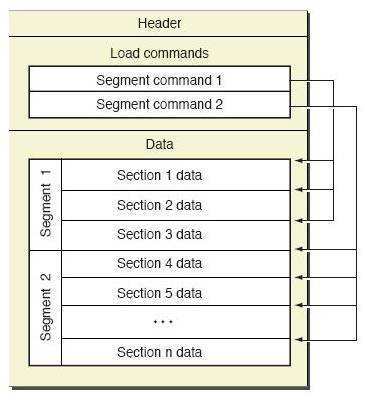
三.Mach-O文件格式
典型的Mach-O文件包含三个区域:
1.Header:保存Mach-O的一些基本信息,包括平台、文件类型、指令数、指令总大小,dyld标记Flags等等。
2.Load Commands:紧跟Header,加载Mach-O文件时会使用这部分数据确定内存分布,对系统内核加载器和动态连接器起指导作用。
3.Data:每个segment的具体数据保存在这里,包含具体的代码、数据等等。
四.其数据结构
1.Header
/*
* The 32-bit mach header appears at the very beginning of the object file for
* 32-bit architectures.
*/
struct mach_header {
uint32_t magic; /* mach magic number identifier */
cpu_type_t cputype; /* cpu specifier */
cpu_subtype_t cpusubtype; /* machine specifier */
uint32_t filetype; /* type of file */
uint32_t ncmds; /* number of load commands */
uint32_t sizeofcmds; /* the size of all the load commands */
uint32_t flags; /* flags */
};
/* Constant for the magic field of the mach_header (32-bit architectures) */
#define MH_MAGIC 0xfeedface /* the mach magic number */
#define MH_CIGAM 0xcefaedfe /* NXSwapInt(MH_MAGIC) */
/*
* The 64-bit mach header appears at the very beginning of object files for
* 64-bit architectures.
*/
struct mach_header_64 {
uint32_t magic; /* mach magic number identifier */
cpu_type_t cputype; /* cpu specifier */
cpu_subtype_t cpusubtype; /* machine specifier */
uint32_t filetype; /* type of file */
uint32_t ncmds; /* number of load commands */
uint32_t sizeofcmds; /* the size of all the load commands */
uint32_t flags; /* flags */
uint32_t reserved; /* reserved */
};
/* Constant for the magic field of the mach_header_64 (64-bit architectures) */
#define MH_MAGIC_64 0xfeedfacf /* the 64-bit mach magic number */
#define MH_CIGAM_64 0xcffaedfe /* NXSwapInt(MH_MAGIC_64) */从上面的代码可以得到如下的解释
| 名称 | 含义 |
| magic | Mach-O魔数,FAT:0xcafebabeARMv7:0xfeedface,ARM64:0xfeedfacf |
| cputype、cpusubtype | CPU架构及子版本 (如CPU_TYPE_X86_64) |
| filetype | MH_EXECUTABLE(可执行二进制文件)、MH_OBJECT(目标文件)、MH_DYLIB(动态库),有11种宏定义类型,具体可查看源码 |
| ncmds | 加载命令的数量 |
| sizeofcmds | 所有加载命令的大小 |
| flags | dyld加载需要的一些标记,有28种宏定义,具体看源码,其中MH_PIE表示启用ASLR地址空间布局随机化 |
| flags | 64位保留字段 |
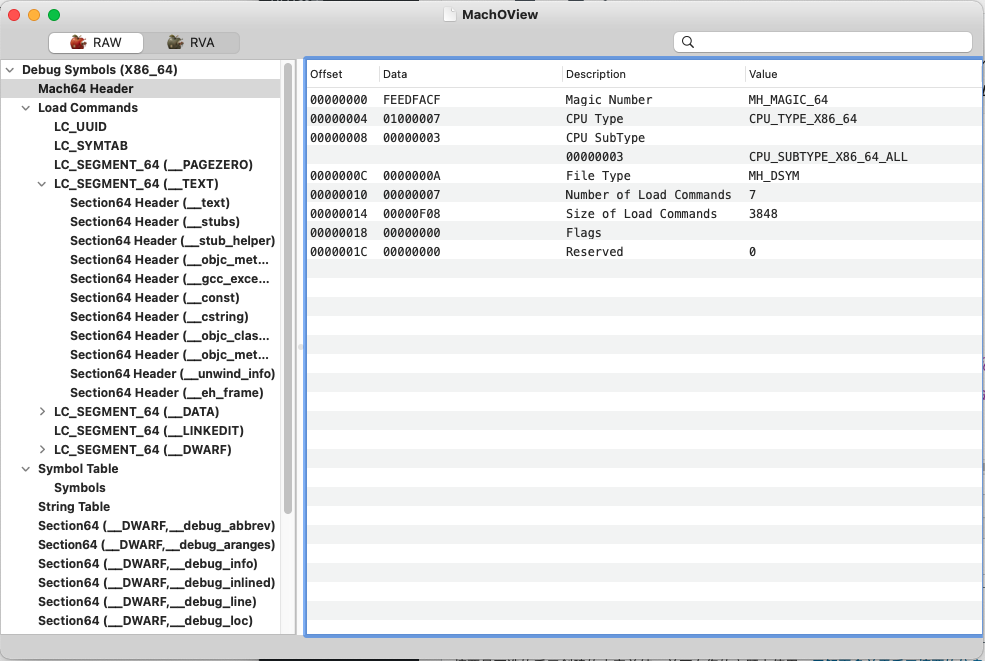
我们可以使用MachOview查看具体的可执行文件的详细情况
MachOview
官方GITHUB地址:https://github.com/gdbinit/MachOView
国人做的改版(支持中文显示):https://github.com/zhongjianfeipqy/MachOView
可以直接运行的编译后版本:http://sourceforge.net/projects/machoview/
2.Load Commands
/*
* The load commands directly follow the mach_header. The total size of all
* of the commands is given by the sizeofcmds field in the mach_header. All
* load commands must have as their first two fields cmd and cmdsize. The cmd
* field is filled in with a constant for that command type. Each command type
* has a structure specifically for it. The cmdsize field is the size in bytes
* of the particular load command structure plus anything that follows it that
* is a part of the load command (i.e. section structures, strings, etc.). To
* advance to the next load command the cmdsize can be added to the offset or
* pointer of the current load command. The cmdsize for 32-bit architectures
* MUST be a multiple of 4 bytes and for 64-bit architectures MUST be a multiple
* of 8 bytes (these are forever the maximum alignment of any load commands).
* The padded bytes must be zero. All tables in the object file must also
* follow these rules so the file can be memory mapped. Otherwise the pointers
* to these tables will not work well or at all on some machines. With all
* padding zeroed like objects will compare byte for byte.
*/
struct load_command {
uint32_t cmd; /* type of load command */
uint32_t cmdsize; /* total size of command in bytes */
};大致翻译:
打开区域显示内容为:
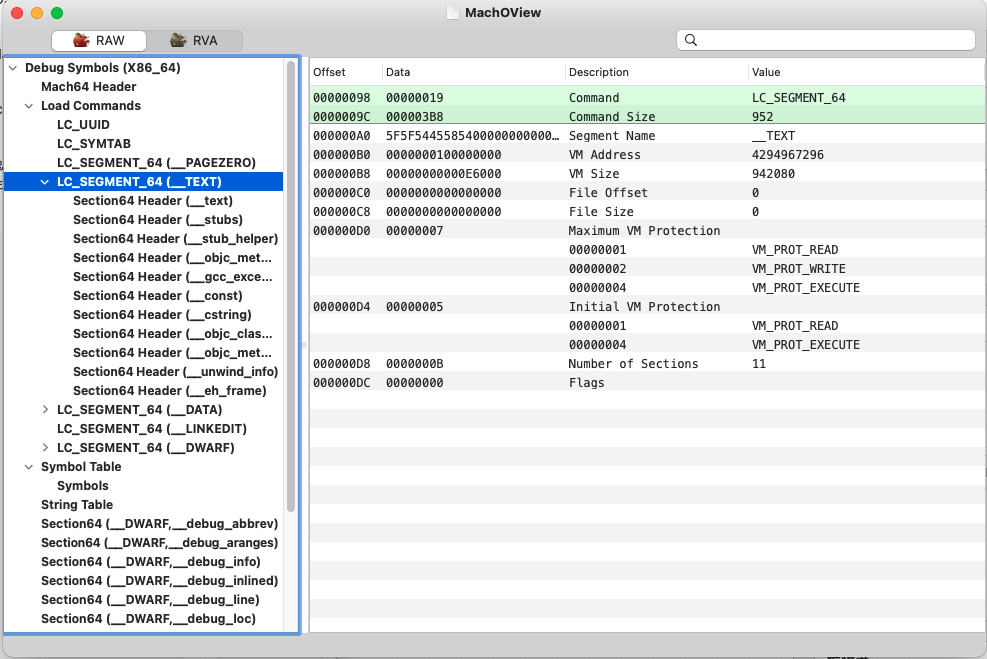
| 指令 | 含义 |
| LC_SEGMENT_64 | 定义一段(Segment),加载后被映射到进程的内存空间中,包括里面的节(Section) |
| LC_SEGMENT_64 | 记录有关链接的信息,包括在__LINKEDIT中动态链接的相关信息的具体偏移与大小(重定位,绑定,弱绑定,懒加载绑定,导出信息等),ONLY表示该指令是程序运行所必需的。 |
| LC_SYMTAB | 定义符号表和字符串表,链接文件时被dyld使用,也用于调试器映射符号到源文件。符号表定义的本地符号仅用于调试,而已定义和未定义的external符号被链接器使用 |
| LC_DYSYMTAB | 将符号表中给出符号的额外信息提供给dyld |
| LC_LOAD_DYLINKER | dyld的默认路径 |
| LC_UUID | Mach-O唯一ID |
| LC_VERSION_MIN_IPHONES | 系统要求的(Iphone【IOS】)最低版本 |
| LC_SOURCE_VERSION | 构建二进制文件的源代码版本号 |
| LC_MAIN | 应用程序入口,dyld的_main函数获取该地址,然后跳转 |
| LC_ENCRYPTION_INFO_64 | 文件加密标志,加密内容偏移和大小 |
| LC_LOAD_DYLIB | 依赖的动态库,含动态库名,版本号等信息 |
| LC_RPATH | @rpath搜索路径 |
| LC_DATA_IN_CODE | 定义在代码段内的非指令的表 |
| LC_CODE_SIGNATURE | 代码签名信息 |
/*
* The 64-bit segment load command indicates that a part of this file is to be
* mapped into a 64-bit task's address space. If the 64-bit segment has
* sections then section_64 structures directly follow the 64-bit segment
* command and their size is reflected in cmdsize.
*/
struct segment_command_64 { /* for 64-bit architectures */
uint32_t cmd; /* Load Command类型 */
uint32_t cmdsize; /*包含的所有section结构体的大小 */
char segname[16]; /* 段名 */
uint64_t vmaddr; /* 映射到虚拟地址的偏移 */
uint64_t vmsize; /* 映射到虚拟地址的大小 */
uint64_t fileoff; /* 相对于当前架构文件的偏移 */
uint64_t filesize; /* 文件大小 */
vm_prot_t maxprot; /* 段页面的最高内存保护 */
vm_prot_t initprot; /* 初始内存保护 */
uint32_t nsects; /* 包含的section数 */
uint32_t flags; /* 段页面标志 */
};主要有一下四种
| 段 | 含义 |
| _PAGEZERO | 空指针陷阱段,映射到虚拟内存空间第一页,捕捉对NULL指针的引用 |
| _TEXT | 代码段、只读数据段 |
| _DATA | 读取和写入数据段 |
| _LINKEDIT | dyld需要使用的信息,包括重定位、绑定、懒加载信息等 |
注:dylib过后补一篇文章做笔记
3.数据区(DATA)

struct section_64 { /* for 64-bit architectures */
char sectname[16]; /* 节名 */
char segname[16]; /* 所属段名 */
uint64_t addr; /* 映射到虚拟地址的偏移 */
uint64_t size; /* 节的大小 */
uint32_t offset; /* 节在当前架构文件中的偏移 */
uint32_t align; /* 节的字节对齐大小n,2^n */
uint32_t reloff; /* 重定位入口的文件偏移 */
uint32_t nreloc; /* 重定位入口个数 */
uint32_t flags; /* 节的类型和属性*/
uint32_t reserved1; /* reserved (for offset or index) */
uint32_t reserved2; /* reserved (for count or sizeof) */
uint32_t reserved3; /* 保留位,以上两同理 */
};
大致有如下内容:
__TEXT:
| __TEXT节 | 含义 |
| __text | 程序可执行代码区域 |
| __stubs | 间接符号存根,用于跳转到懒加载指针表 |
| __stubs_helper | 懒加载符号加载辅助函数 |
| __cstring | 只读的C字符串,包含OC的部分字符串和属性名 |
| ...... | …… |
__DATA:
| __DATA | 含义 |
| __nl_symbol_ptr | 非懒加载指针表,dyld加载时立即绑定值 |
| __la_symbol_ptr | 懒加载指针表,第1次调用才绑定值 |
| __got | 非懒加载全局指针表 |
| __mod_init_func | constructor函数 |
| __cfstring | OC字符串 |
| …… | …… |
挑选一些进行详细介绍
1). (__TEXT,__text)
这里存放的是汇编后的代码,当我们进行编译时,每个.m文件会经过预编译->编译->汇编形成.o文件,称之为目标文件。汇编后,所有的代码会形成汇编指令存储在.o文件的(__TEXT,__text)区((__DATA,__data)也是类似)。链接后,所有的.o文件会合并成一个文件,所有.o文件的(__TEXT,__text)数据都会按链接顺序存放到应用文件的(__TEXT,__text)中。
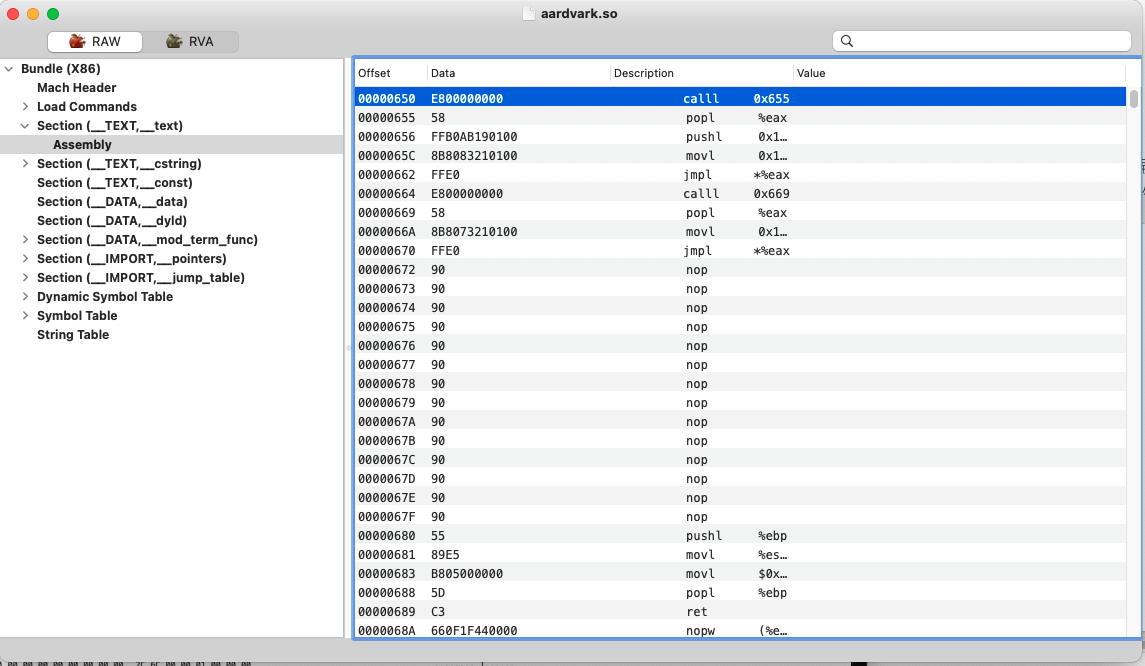
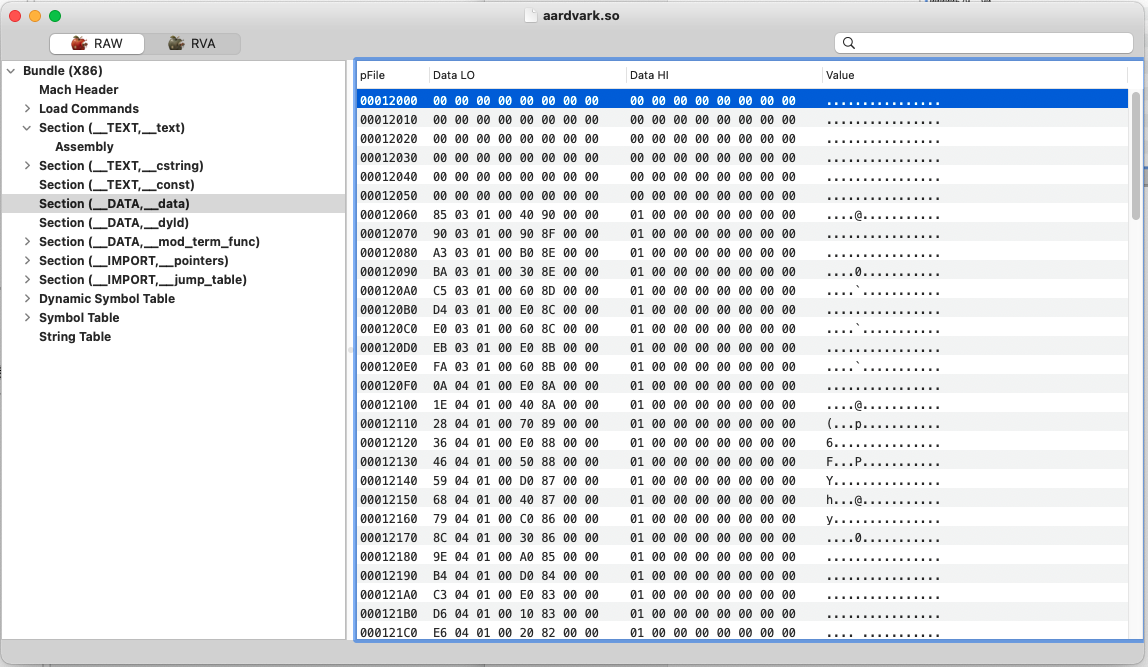
2). (__DATA,__data)
存储数据的section,static在进行非零赋值后会存储在这里,如果static 变量没有赋值或者赋值为0,那么它会存储在(__DATA,__bss)中。
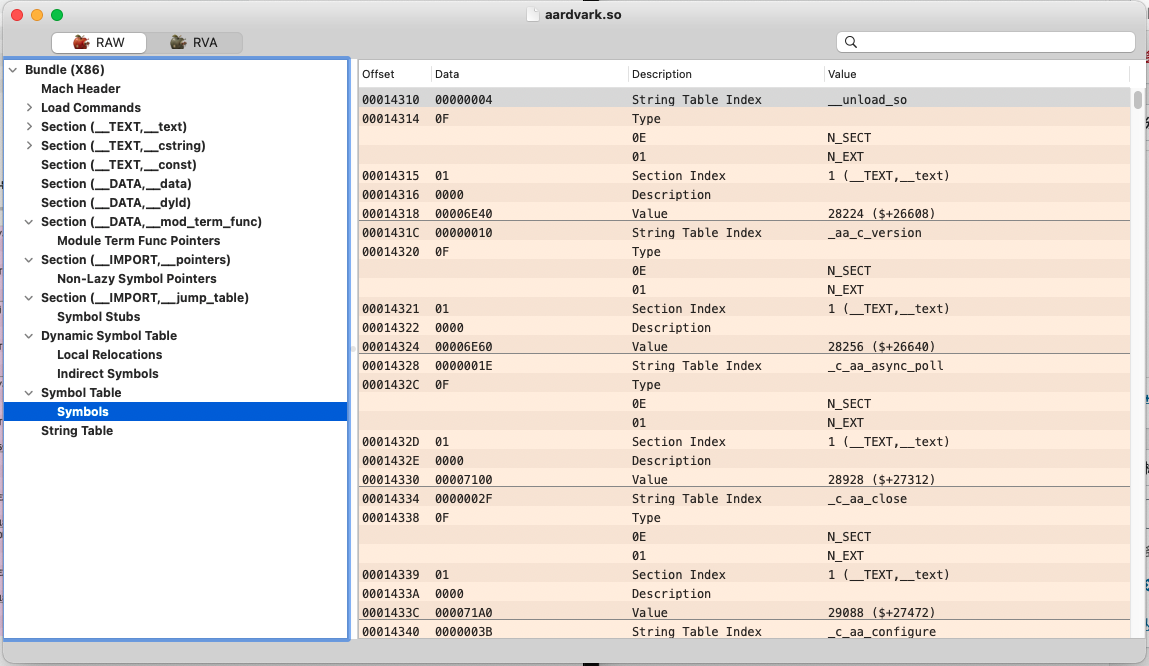
3). Symbol Table
符号表,这个是重点中的重点,符号表是将地址和符号联系起来的桥梁。符号表并不能直接存储符号,而是存储符号位于字符串表的位置。
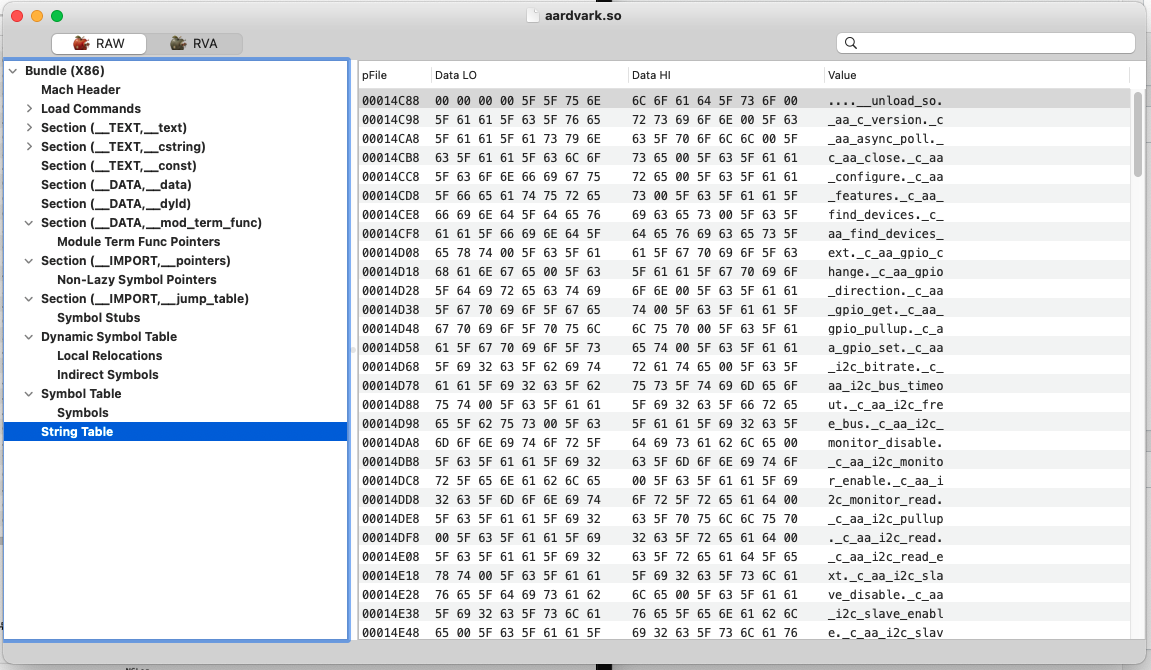
4). String Table
字符串表所有的变量名、函数名等,都以字符串的形式存储在字符串表中。
5). Indirect Symbols (动态符号表)
动态符号表存储的是动态库函数位于符号表的偏移信息。(__DATA,__la_symbol_ptr) section 可以从动态符号表中获取到该section位于符号表的索引数组。
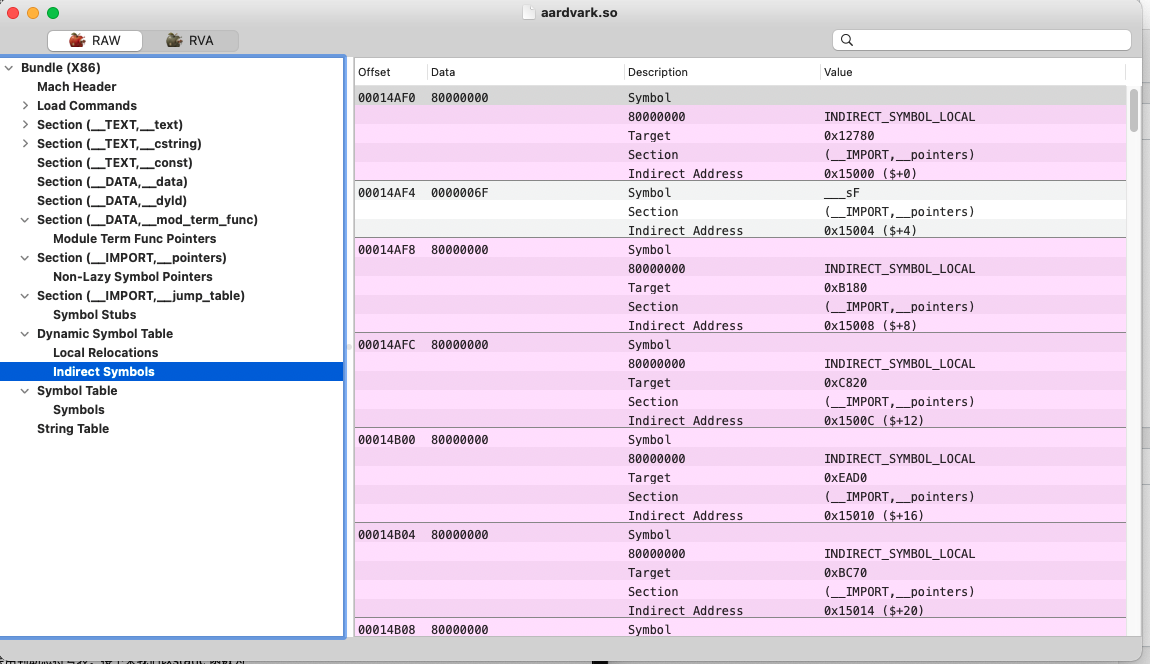
动态符号表并不存储符号信息,而是存储其位于符号表的偏移信息。Fishhook源码看起来比较复杂主要是因为hook的是动态链接的函数,索引和链接关系比较绕。但是我们自己编写的C函数不是动态链接的,而是在编译链接后代码指令就存储在文件内部的函数,因此不会用到动态符号表。接下来我们以static 函数为例,看看如何动态的查找自己编写的函数地址。
参考:
https://www.jianshu.com/p/5a44f69466cc
https://www.cnblogs.com/dengzhuli/p/9952202.html
https://baike.baidu.com/item/Mach-O/9608283?fr=aladdin
https://www.jianshu.com/p/c51a138c932f?open_source=weibo_search【优化MachOView】
0 条评论